Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
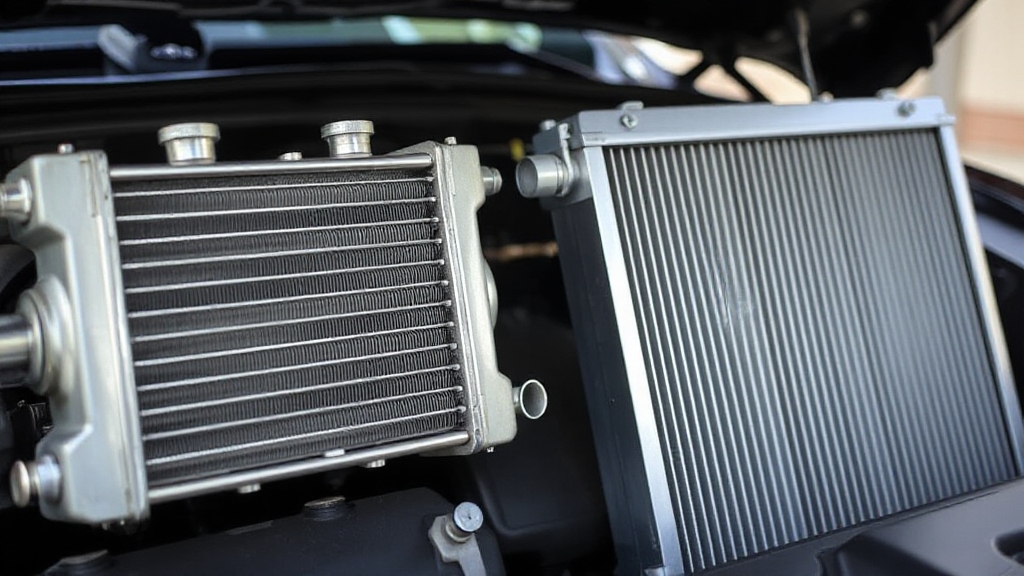
You’ll find that an internal transmission cooler in the radiator offers basic heat management by exchanging heat with engine coolant, ideal for normal driving and light towing.
However, an external transmission cooler, mounted separately with dedicated airflow, provides superior heat dissipation critical for heavy towing, high-performance use, or extreme conditions.
While internal coolers simplify installation, external units better prevent overheating and extend transmission life under stress. Understanding their distinct roles helps optimize cooling strategies and system longevity.
| Feature | Internal Radiator Cooler | External Transmission Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Capacity | Basic cooling for standard driving | Superior heat dissipation for heavy loads |
| Installation | Pre-integrated – no setup required | Requires custom mounting and fluid lines |
| Cost | No additional cost | Additional expense for purchase and installation |
| Best Use Cases | Normal driving, light towing | Heavy towing, extreme conditions, performance use |
| Maintenance | Minimal – integrated system | Requires regular cleaning and inspection |
| Durability | Protected within radiator housing | More vulnerable to road debris |
| Performance Under Load | Adequate for everyday use | Essential for demanding applications |
Although you mightn’t notice it at first glance, the internal transmission cooler is a crucial component embedded within the radiator that efficiently manages transmission fluid temperature.
This cooler consists of small brass or copper tubing housed inside the radiator tank, where transmission fluid flows through narrow passages surrounded by engine coolant. This positioning maximizes heat exchange, as the coolant absorbs heat directly from the transmission fluid.
The tube’s thin wall, approximately 1/32 inch thick, allows transmission fluid to form a thin sheet, increasing surface contact and enhancing heat transfer efficiency.
Many high-performance oils, such as those with advanced additive technology, benefit from effective cooling systems to maintain optimal operation.
The radiator’s durable housing ensures protection and longevity. By immersing the transmission fluid in coolant rather than air, the design achieves superior heat transfer, maintaining ideal fluid temperatures.
This integration saves space, reduces system complexity, and supports standard driving and moderate towing conditions without additional cooling units, ensuring consistent transmission performance and preventing overheating.
While the internal transmission cooler integrated within the radiator manages fluid temperature under normal conditions, vehicles facing heavy loads or towing demands often require additional cooling capacity.
An external transmission cooler lowers fluid temperature by routing hot transmission fluid through tubes surrounded by heat-dissipating fins. These coolers are essential because they help prevent transmission failure caused by overheating under strenuous driving conditions.
Selecting quality fluids like Pennzoil’s synthetic base oil can further enhance cooling efficiency and engine protection. As fluid flows through, heat transfers from the tubes to the fins, which dissipate it into the surrounding air.
Positioned where airflow is ideal typically in front of the radiator or grille these coolers maximize heat exchange efficiency. After cooling, the fluid returns to the transmission, maintaining the best operating temperatures and preventing overheating.
Their design, often tube-and-fin, balances compactness with effective heat transfer, supplementing internal coolers during high thermal loads to preserve fluid integrity and transmission component longevity.
Because external transmission coolers offer substantially greater surface area than internal radiator coolers, they extract heat from transmission fluid more effectively, especially under heavy loads or high-performance conditions.
This enhanced cooling capability aligns with the benefits seen in AMSOIL Gear Oil applications, which are designed to provide advanced protection against wear in extreme temperatures.
Internal coolers share heat dissipation with engine coolant, limiting their capacity as coolant temperature and radiator size constrain efficiency. In contrast, external coolers leverage direct ambient airflow, independently optimizing heat rejection and reducing transmission fluid temperature more notably.
This separation also lessens thermal stress on the radiator, enhancing overall engine cooling stability. Additionally, increased engine torque and horsepower elevate stress and heat, making external coolers even more beneficial for upgraded vehicles.
However, internal coolers provide adequate performance in mild conditions by integrating warming and cooling functions within the radiator.
For elevated thermal demands, external coolers offer superior temperature control, extending transmission longevity by minimizing fluid breakdown and wear through more consistent, effective heat dissipation.
When installing an external transmission cooler, you must prioritize mounting it in a location with ideal airflow, typically in front of the radiator, to maximize heat dissipation. Avoid restricted airflow areas to prevent transmission fluid overheating.
Proper placement enhances cooling performance by ensuring sufficient air circulation around the cooler. It is also important to consider the vapor pressure of transmission fluid when selecting compatible hoses to avoid degradation under heat.
Secure the cooler using brackets or clamps to eliminate vibration damage. Position fittings on the top or sides, never pointing downward, to prevent air pockets that impair cooling efficiency.
Mount the cooler firmly with brackets and orient fittings upwards to avoid air pockets and vibration damage.
Route transmission lines carefully, avoiding sharp bends or kinks to maintain fluid flow. Measure line diameters accurately and use appropriate compression fittings with thread sealant, tightening securely without over-torquing.
Use hoses rated for transmission fluid and heat exposure to ensure durability. Proper integration with the radiator’s cooling system requires routing fluid first through the radiator cooler, then the external cooler, optimizing overall transmission cooling performance.
Although external transmission coolers rely on airflow to dissipate heat, internal transmission coolers use engine coolant to regulate transmission fluid temperature more precisely.
By circulating coolant through the radiator, they warm the fluid to ideal operating temperature faster, reducing wear from cold, viscous fluid. This helps maintain the viscosity ratings necessary for optimal transmission performance.
This precise temperature control stabilizes fluid viscosity, prevents thermal breakdown, and minimizes oxidation and sludge formation. Maintaining fluid within perfect temperature limits greatly extends transmission lifespan by slowing fluid degradation and reducing stress on components like clutches and seals.
An internal cooler also prevents transmission overheating by efficiently managing fluid temperature during heavy-duty use. You’ll notice improved gear shift smoothness and power delivery, essential during demanding conditions such as towing or stop-and-go traffic.
Integrated within the radiator system, internal coolers simplify installation and reduce maintenance costs while providing reliable thermal management that supports consistent transmission performance and durability.
Internal transmission coolers effectively regulate fluid temperature through engine coolant circulation, but they may not suffice under extreme thermal demands. Avoid mixing brake fluid with hydraulic fluid as it can cause system damage and failure due to their differing compatibility requirements.
External transmission coolers offer superior heat dissipation due to their larger surface area and independent airflow, making them essential for towing or heavy loads.
However, they require careful installation to maintain fluid flow and prevent leaks, as exposure increases vulnerability to damage. Regular upkeep such as oil changes, flushing, and inspections is necessary to ensure cooler effectiveness and avoid issues related to maintenance neglect.
Consider these points:
You’ll enhance transmission longevity by combining internal and external cooling systems, as each targets different temperature demands.
Proper installation matter;s fluid should flow from the transmission through the radiator cooler first, then the external cooler, to optimize heat dissipation without causing pressure drops. This setup maintains stable fluid viscosity, reduces thermal stress, and boosts overall drivetrain efficiency under variable loads.
Using oils with appropriate wear protection additives can further improve cooling system performance by reducing friction and heat generation.
Additionally, because transmission coolers often require an external pump and filter, ensuring these components function properly is crucial for effective oil circulation and cooling.
When you combine internal radiator coolers with external transmission coolers, you achieve rapid and precise control over transmission fluid temperatures.
The internal cooler handles baseline heat dissipation, maintaining stable fluid temperatures during normal driving. Proper temperature regulation is crucial to prevent fluid degradation and maintain optimal performance.
The external cooler activates under heavy load, preventing thermal spikes by further reducing fluid heat. This staged cooling system enhances transmission efficiency and longevity by minimizing fluid degradation and wear.
Key benefits of dual cooling include:
This integrated approach optimizes cooling capacity, ensuring transmission reliability in demanding applications.
Combining internal radiator coolers with external transmission coolers demands careful installation to maximize cooling efficiency and system reliability. Position the external cooler at the vehicle front with foam rubber pads to isolate it from the radiator and prevent vibration damage.
Route fluid from the transmission outlet to the cooler’s top inlet, then back through the radiator’s internal cooler for staged cooling, avoiding sharp bends and ensuring secure fittings.
Use corrosion-resistant hardware with lock washers to maintain stability under vibration. Proper clearance prevents component contact and promotes airflow, preserving both cooling functions without thermal interference.
For optimal performance, selecting the appropriate oil viscosity is essential, as it influences the cooling and lubrication characteristics of transmission fluids, much like how viscosity range impacts engine oil performance.
| Aspect | Best Practice | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting | Foam pads, quick-fit rods | Vibration isolation, secure attachment |
| Fluid Routing | External cooler first, then internal | Optimized staged cooling |
| Hardware | Corrosion-resistant, lock washers | Long-term durability |
Although internal transmission coolers quickly bring fluid to an ideal temperature using engine coolant, relying solely on them can limit cooling capacity under heavy loads.
Combining an internal cooler with a properly sized external cooler optimizes performance by rapidly reaching operating temperature and efficiently dissipating excess heat during demanding conditions.
This dual system stabilizes fluid temperature, reducing wear on seals and valves, and extends transmission lifespan, especially in towing or high-performance scenarios.
Note that operating transmission fluid within the optimal temperature range of 165-230°F prevents fluid thinning and damage that can lead to costly repairs.
Proper cooling also helps maintain the hydraulic oil’s viscosity, ensuring reliable hydraulic system performance. Key benefits include:
Since transmission fluid temperature directly affects component wear and fluid integrity, effective cooling substantially enhances transmission longevity and reliability.
By preventing fluid overheating, cooling systems reduce premature wear on bearings, clutch packs, and gears, maintaining ideal lubrication and preventing thermal breakdown.
Transmission coolers extract heat from the fluid to maintain optimal temperature, thereby preventing overheating and prolonging transmission lifespan.
External coolers, with their larger surface area, dissipate heat more efficiently under heavy loads, while radiator coolers stabilize fluid temperature in varying climates. This dual approach minimizes fluid degradation and contamination, preserving filter performance and internal cleanliness.
Consequently, you’ll experience fewer transmission slips and harsh shifts, improving drivability and reducing costly repairs. Furthermore, maintaining stable thermal conditions protects sensors and electronics, ensuring reliable diagnostics and system control.
When determining the appropriate transmission cooling system for your vehicle, you must analyze how you use it and the associated thermal demands.
For light-duty vehicles with standard driving, an internal radiator cooler usually suffices, providing balanced fluid temperatures without overcooling.
However, if you frequently tow heavy loads, drive in hot or mountainous regions, or operate in stop-and-go traffic, an external transmission cooler becomes essential to prevent overheating and maintain fluid viscosity.
Among external coolers, tube and fin coolers are the most common and cost-effective choice for moderate needs. Consider these factors when selecting your cooling system:
Choosing the right cooler tube and fin, plate and fin, or stacked plate, depends on balancing efficiency, cost, and durability tailored to your specific driving conditions.
Yes, you can add an external transmission cooler without removing the radiator. Typically, the external cooler mounts separately, often in front of the radiator, allowing airflow to dissipate heat effectively.
This setup supplements the internal cooler inside the radiator, maintaining original functions. You just need to guarantee proper sizing and secure fluid lines for maximum performance.
This approach simplifies installation and enhances transmission cooling, especially under heavy load or towing conditions.
Imagine towing a heavy trailer uphill; your transmission fluid heats up quickly. By installing a transmission cooler, you reduce fluid temperature, which lowers transmission drag and improves shift responsiveness.
This decreases engine workload, directly enhancing fuel efficiency. Cooler fluid prevents overheating, extending transmission life and maintaining ideal operation.
When you maintain an external transmission cooler, you coincidentally guarantee your transmission’s longevity and performance. You’ll want to clean the cooler fins regularly using compressed air or gentle washing to remove dirt and debris.
Inspect mounting brackets for corrosion or looseness, and check for leaks or punctures in the core. Confirm good airflow at the mounting location and replace damaged parts promptly. These steps prevent overheating and fluid contamination, keeping your system efficient.
Yes, an external cooler can cause transmission fluid leaks. You need to inspect seals, gaskets, and fittings regularly since deterioration or damage can create weak points.
Vibrations, thermal cycling, and environmental exposure increase the risk of cracks or loose connections in cooling lines. Poor-quality aftermarket coolers or improper installation further elevate leak potential.
Catching these issues early prevents fluid loss, overheating, and transmission damage. Regular maintenance is essential to maintain system integrity.
So, you could just trust your radiator’s internal transmission cooler to do all the heavy lifting—after all, it’s been “working fine” for years, right? But when your transmission’s heat climbs like a summer highway, relying solely on that might be a gamble.
Installing an external cooler isn’t just extra gear; it’s a calculated upgrade that sharply boosts cooling efficiency and transmission longevity. Sometimes, doubling down on cooling isn’t overkill—it’s smart engineering.
Last update on 2026-03-14 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API